I know that what I'm about to say doesn't take a PhD to understand because, well, I don't have a PhD!
Here goes:
A parking lane is a place for vehicles to park. It is not a place to drive.
A vehicle lane is a place to operate vehicles. It is not a place to park.
A bicycle is a vehicle.
Therefore, a bicycle lane is not a place to park.
That, essentially, is the straightforward argument set out in an article D'val Westphal wrote for the Albuquerque Journal.
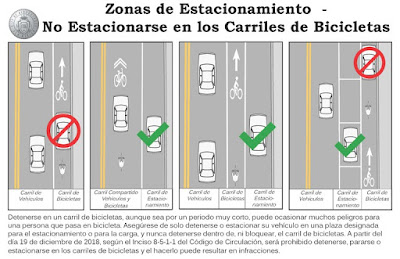
Members of the Albuquerque City Council understand that argument. In fact, they have even made an ordinance, which will go into effect on the 19th of this month, based on it. Better yet, for those of us who don't like to (or can't) read legalese, they've made a graphic of it, with captions in both English and Spanish.
Thank you, Albuquerque City Council and D'val Westphal.
Now we have to get folks in other cities to codify--and enforce--such rules. If they need guidance, they can listen to this cheesy pop song from my pubescence:
Here goes:
A parking lane is a place for vehicles to park. It is not a place to drive.
A vehicle lane is a place to operate vehicles. It is not a place to park.
A bicycle is a vehicle.
Therefore, a bicycle lane is not a place to park.
That, essentially, is the straightforward argument set out in an article D'val Westphal wrote for the Albuquerque Journal.
Members of the Albuquerque City Council understand that argument. In fact, they have even made an ordinance, which will go into effect on the 19th of this month, based on it. Better yet, for those of us who don't like to (or can't) read legalese, they've made a graphic of it, with captions in both English and Spanish.
Thank you, Albuquerque City Council and D'val Westphal.
Now we have to get folks in other cities to codify--and enforce--such rules. If they need guidance, they can listen to this cheesy pop song from my pubescence: